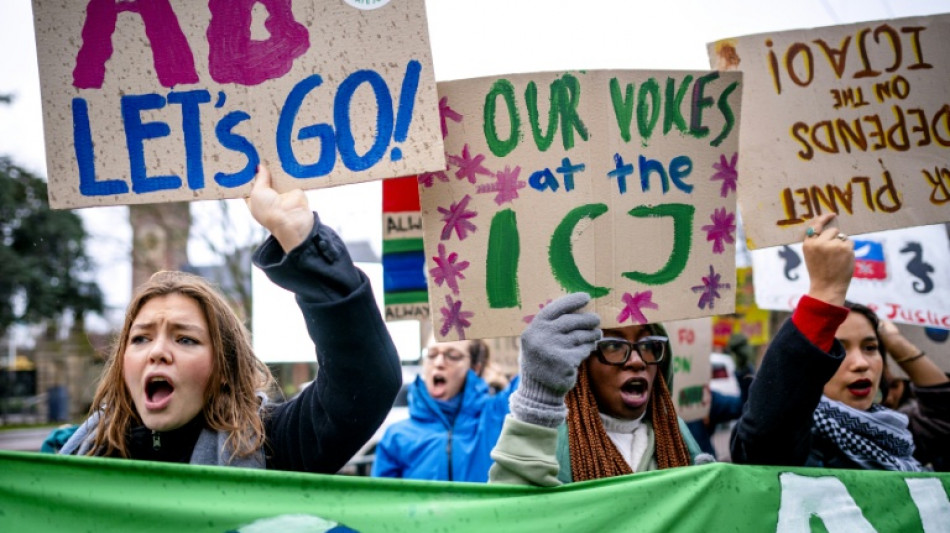
JRI
0.2135

The world's highest court Wednesday declared that states have a legal obligation to tackle climate change and that failing to do so was a "wrongful act" that could open the door to reparations.
The decision by the International Court of Justice was closely watched by legal experts, who said the judges' opinion could mark a turning point for environmental justice and climate litigation around the world.
ICJ advisory opinions are not binding but carry considerable moral and legal weight, and Wednesday's decision was seen as the most consequential in a recent string of landmark climate rulings.
The United Nations had tasked the 15 judges at the ICJ, a UN court in the Hague that adjudicates disputes between nations, to answer two fundamental questions.
First: what must states do under international law to protect the environment from greenhouse gas emissions "for present and future generations"?
Second: what are the consequences for states whose emissions have caused environmental harm, especially to vulnerable low-lying island states?
In handing down the decision, ICJ president Yuji Iwasawa said climate change was an "urgent and existential threat" and states breaching their obligations to address the crisis were committing "an internationally wrongful act".
"The legal consequences resulting from the commission of an internationally wrongful act may include... full reparations to injured states in the form of restitution, compensation and satisfaction," the court said.
This would be on a case-by-case basis where a "sufficient direct and certain causal nexus" had been shown "between the wrongful act and the injury", it added.
It also said the climate "must be protected for present and future generations" and the adverse effect of a warming planet "may significantly impair the enjoyment of certain human rights, including the right to life".
Experts said it would take time to go over the full advisory opinion, which is the biggest case ever handled by the ICJ.
To reach its decision, ICJ judges pored over tens of thousands of pages of submissions from countries and organisations around the world.
- 'No more delay' -
Outside the court in the Hague, about a hundred demonstrators waved flags and posters bearing slogans like "No more delay, climate justice today".
Courts have become a key battleground for climate action as frustration has grown over sluggish progress toward curbing planet-warming pollution from fossil fuels.
The Paris Agreement struck through the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has rallied a global response to the crisis, but not at the speed necessary to protect the world from dangerous overheating.
The journey to the world's highest court was six years in the making, spearheaded by students from the climate-imperilled Pacific region, and championed by tiny island nation Vanuatu.
Ahead of the ruling, Vanuatu's climate change minister Ralph Regenvanu said the advisory opinion could be a "game-changer".
"We've been going through this for 30 years... It'll shift the narrative, which is what we need to have," Regenvanu told AFP.
More than 100 nations and groups gave submissions at a mammoth hearing in December in the Great Hall of Justice in the Hague.
Many hailed from distant Pacific Island nations, and delivered impassioned appeals in the sober arena dressed in colourful traditional attire.
The debate pitted major wealthy economies against the smaller, less developed states most at the mercy of a warming planet.
Big polluters including the United States and India argued that legal provisions under the UNFCCC were sufficient and a re-examination of state responsibility in relation to climate action was not necessary.
But smaller states refuted this, saying the UN framework was inadequate to mitigate climate change's devastating effects and that the ICJ's opinion should be broader.
These states also urged the ICJ to impose reparations on historic polluters, a highly sensitive issue in global climate negotiations.
They also demanded a commitment and timeline to phasing out fossil fuels, monetary compensation when appropriate, and an acknowledgement of past wrongs.
Ahead of the decision, experts said the advisory opinion could have ripple effects across national courts, legal processes, and public debate.
G.Tsang--ThChM