RYCEF
-0.0600


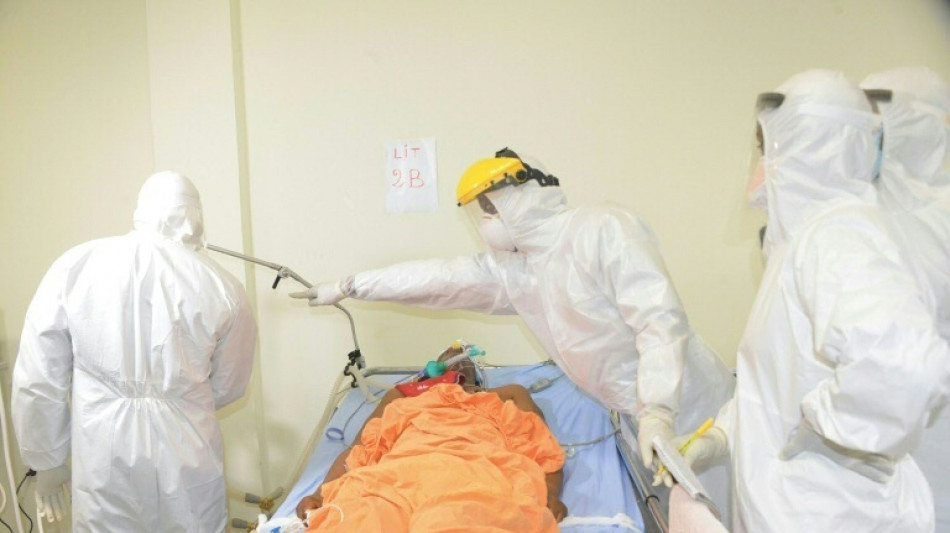
Seven people have been killed in an outbreak of Marburg virus in Equatorial Guinea, with a further 20 deaths "probably" due to the hemorrhagic fever, the World Health Organization said Thursday.
The outbreak of the virus, which is almost as deadly as Ebola, has now spread beyond the province of Kie-Ntem, where it caused the first known deaths in January.
It has reached Bata, the economic capital of the small central African country, according to the government.
The spread of Marburg "is a critical signal to scale up response efforts to quickly stop the chain of transmission and avert a potential large-scale outbreak and loss of life," said Dr Matshidiso Moeti, the WHO's regional director for Africa.
Since the start of the outbreak, "there have been a total of nine laboratory-confirmed cases and 20 probable cases", the WHO said in a report on its website.
"Of the nine laboratory-confirmed cases, seven people have died and all probable cases have died."
Among the 20 probable cases, the patients had all the symptoms of the disease and had been in contact with confirmed cases, but samples could not be taken from their bodies, or they could not be treated, a WHO official told AFP Thursday.
The new cases have been reported from Kie-Ntem in the east, Litoral in the west and the Centro Sur provinces, all of which have borders with Cameroon and Gabon.
The epidemic is therefore now a serious problem in three of Equatorial Guinea's four mainland provinces.
- 'High alert' -
In eastern Africa, Tanzania said Tuesday that five people had died from the virus, while neighbouring Uganda, which had its last outbreak in 2017, said it was on "high alert".
The WHO said additional experts in epidemiology, logistics, health operations and infection prevention and control would be deployed in the coming days.
The agency is also supporting the health authorities in neighbouring Cameroon and Gabon to ramp up outbreak readiness and response capabilities.
The Marburg virus causes severe fever, often accompanied by bleeding and organ failure.
It is part of the so-called filovirus family that also includes Ebola, which has wreaked havoc in several previous outbreaks in Africa.
The suspected natural source of the Marburg virus is the African fruit bat, which carries the pathogen but does not fall sick from it.
The virus takes its name from the German city of Marburg, where it was first identified in 1967, in a lab where workers had been in contact with infected green monkeys imported from Uganda.
The animals can pass the virus to primates in close proximity, including humans, and human-to-human transmission then occurs through contact with blood or other body fluids.
Fatality rates in confirmed cases have ranged from 24 percent to 88 percent in previous outbreaks, depending on the virus strain and case management, according to WHO.
There are currently no vaccines or antiviral treatments, but potential treatments, including blood products, immune therapies and drug therapies, as well as early candidate vaccines, are being evaluated, the WHO says.
B.Chan--ThChM