SCS
0.0200


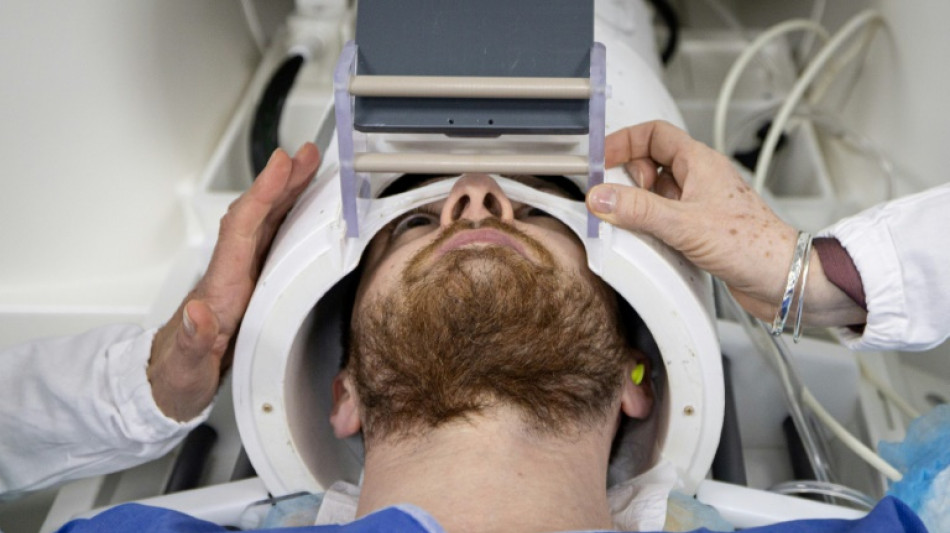
A magnetic resonance imaging device built with off-the-shelf parts and paired with AI matched the performance of high-end MRI machines, according to a study published Thursday that could pave the way for greater access to the life-saving tools.
First introduced five decades ago, MRI scanners are now a cornerstone of modern medicine, vital for diagnosing a wide range of conditions -- including strokes, tumors, and spinal conditions -- while avoiding exposing patients to radiation.
But they remain hard to come by in developing countries: Africa has less than one MRI machine per million people, while the figures in the United States and Japan are 40 and 55 per million, respectively.
To tackle the problem, Yujiao Zhao and colleagues at the University of Hong Kong built a simplified, low-powered MRI machine using store-bought hardware that cost around $22,000, and published their findings in the prestigious journal Science.
MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to align and manipulate the body's hydrogen atoms, producing detailed images of internal structures and organs.
The strength of magnets is measured in units called teslas (T), with conventional MRIs requiring powerful electromagnets that have wires bathed in supercooled liquid helium to generate magnetic fields of 1.5T to 7T.
These machines demand high electricity inputs, far exceeding what standard wall outlets can provide, and must be housed in radio frequency-shielded rooms to prevent equipment interference. Current clinical use MRIs cost upwards of million dollars.
By contrast, the Hong Kong research team's full body MRI machine used a helium-free 0.05T magnet and required just 1800 watts -- comparable to a hair dryer, meaning it could use a standard socket. What's more, it did not require radio shielding.
To compensate for the reduced image detail and higher levels of radio interference, the researchers integrated their system with a deep learning algorithm trained on a vast dataset of high-resolution images of human anatomical structures.
They then tested their machine on 30 healthy adult volunteers, performing scans over their bodies from their brains down to their knees.
The results from their so-called "ultra low field" MRI were found to be on par with conventional MRI scanners 60 times more powerful.
"These advances pave the way for affordable, patient centric, and deep learning–powered ULF MRI scanners, addressing unmet clinical needs in diverse healthcare settings worldwide," Zhao and colleagues wrote.
In an accompanying comment piece, researchers Udunna Anazodo and Stefan du Plessis wrote the approach was "promising" but added several challenges needed to be addressed before it can be widely applied.
"Concerted effort must be taken to develop the skills needed to ensure local production and maintenance of these devices and their proper use," in countries with low resources, they said. Radiologists would also need to be retrained to appropriately interpret the images.
F.Jackson--ThChM