RBGPF
4.4200


The world-first insemination of an Amur leopard in France has lifted hopes of animal lovers for the survival of the Earth's rarest big cat.
The spotted felines, native to the banks of the Siberian river of the same name on the Russian-Chinese border, are believed to number in just scores in the wild.
So the breakthrough procedure undergone last week by Khala, a 15-year-old leopard at Mulhouse Zoo near the German border, has raised expectations that breeding programmes in captivity could save the species.
"This is a world first," said veterinarian Benoit Quintard, director of the Mulhouse Zoological and Botanical Park and coordinator of the European breeding program for the Amur leopard.
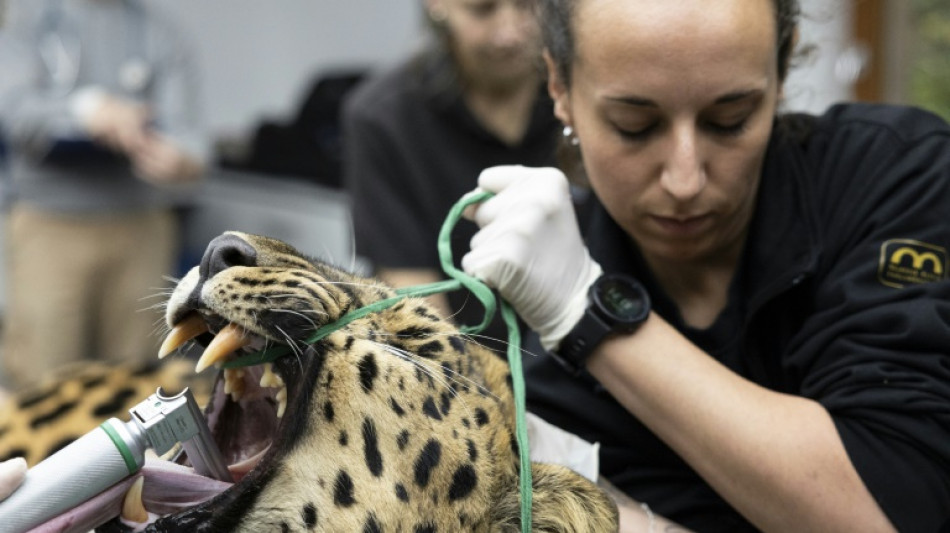
Before Khala's 35-kilogramme (77-pound) frame could be hauled onto the operating table, she had to be sedated -- with the big cat agitating furiously at the sight of the rifle about to shoot an anaesthetic dart.
Minutes later, Khala slept eyes wide open as seven vets set about their work around the leopard, resplendent in black-and-gold fur.
On the morning of the operation Khala had mated once again with Baruto, a 14-year-old male.
But with their couplings so far fruitless, the veterinarians decided to give nature a little nudge.
Baruto, 15 kilogrammes heavier than Khala, was the first on the operating table, with an intravenous drip continuously pumping a cocktail of anaesthetics into his bloodstream to keep him sedated.
- '50-50 chance' -
As Baruto's long dappled tail dangled in the air, Professor Thomas Hildebrandt, on loan from Berlin's Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research, which specialises in the reproduction of endangered species, set about his work.
With a small sample of the leopard's semen extracted, it was Khala's turn to be operated on.
First the vets carried out an ultrasound to check the cat's uterus.
"Good news: she has ovulated. Bad news: there are cysts," Hildebrandt said.
As a result, even if Baruto's sperm fertilises Khala's egg, there is a risk it may not be able to attach itself to the uterus walls.
Nonetheless the vet pressed on. With a probe inserted and a gentle squeeze of the trigger the procedure was complete.
"I think it's about a 50-50 chance that she will be pregnant now," said Susanne Holtze, Hildebrant's colleague from the Leibniz Institute.
After a weigh-in and one last jab, Khala was awake and back in her enclosure, and hopefully three months out from giving birth to a rare feline cub.
- Inbreeding risks -
Classed as "critically endangered" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, the Amur leopard is at risk of habitat loss and the disappearance of some of its prey.
As the population dwindles, the surviving felines have fewer potential mates, heightening the risks of inbreeding.
Khala and Baruto were not chosen at random -- their genetic makeup was considered varied enough to bolster the species' genetic diversity.
Some of Baruto's sample was also kept back by the scientists "so that if anything ever happens to him we still have his genetic pool, potentially for future inseminations", explained Quintard.
The about 250 Amur leopards kept in captivity are crucial to the species as they possess a "far more widespread genetic make-up than those still present in the wild", the veterinarian said.
On the Chinese side of the border, the national forestry board believes there are reasons to be cheerful. Thanks to a conservation drive launched in 2017, Beijing says that the number of leopards in the wild has nearly doubled, from 42 before it began to 80 in 2025.
Yet the elegant felines have become an indirect victim of the war in Ukraine, with a Russian reintroduction programme on pause until further notice.
C.Fong--ThChM