RBGPF
0.1000


David Smith, a retired print technician from the north of England, was pursuing his hobby of looking for interesting shapes when he stumbled onto one unlike any other in November.
When Smith shared his shape with the world in March, excited fans printed it onto T-shirts, sewed it into quilts, crafted cookie cutters or used it to replace the hexagons on a soccer ball -- some even made plans for tattoos.
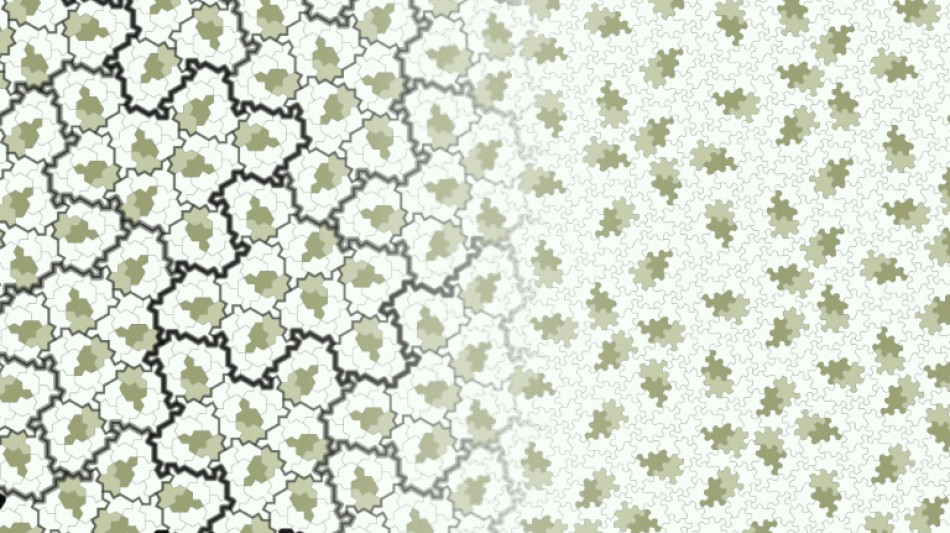
The 13-sided polygon, which 64-year-old Smith called "the hat", is the first single shape ever found that can completely cover an infinitely large flat surface without ever repeating the same pattern.
That makes it the first "einstein" -- named after the German for "one stone" (ein stein), not the famed physicist -- and solves a problem posed 60 years ago that some mathematicians had thought impossible.
After stunning the mathematics world, Smith -- a hobbyist with no training who told AFP that he wasn't great at maths at school -- then did it again.
While all agreed "the hat" was the first einstein, its mirror image was required one in seven times to ensure that a pattern never repeated.
But in a preprint study published online late last month, Smith and the three mathematicians who helped him confirm the discovery revealed a new shape -- "the spectre."
It requires no mirror image, making it an even purer einstein.
- 'It can be that easy' -
Craig Kaplan, a computer scientist at Canada's Waterloo University, told AFP that it was "an amusing and almost ridiculous story -- but wonderful".
He said that Smith, a retired print technician who lives in Yorkshire's East Riding, emailed him "out of the blue" in November.
Smith had found something "which did not play by his normal expectations for how shapes behave", Kaplan said.
If you slotted a bunch of these cardboard shapes together on a table, you could keep building outwards without them ever settling into a regular pattern.
Using computer programs, Kaplan and two other mathematicians showed that the shape continued to do this across an infinite plane, making it the first einstein, or "aperiodic monotile".
When they published their first preprint in March, among those inspired was Yoshiaki Araki. The Japanese tiling enthusiast made art using the hat and another aperiodic shape created by the team called "the turtle", sometimes using flipped versions.
Smith was inspired back, and started playing around with ways to avoid needing to flip his hat.
Less than a week after their first paper came out, Smith emailed Kaplan a new shape.
Kaplan refused to believe it at first. "There's no way it can be that easy," he said.
But analysis confirmed that Tile (1,1) was a "non-reflective einstein", Kaplan said.
Something still bugged them -- while this tile could go on forever without repeating a pattern, this required an "artificial prohibition" against using a flipped shape, he said.
So they added little notches or curves to the edges, ensuring that only the non-flipped version could be used, creating "the spectre".
- 'Hatfest' -
Kaplan said both their papers had been submitted to peer-reviewed journals. But the world of mathematics did not wait to express its astonishment.
Marjorie Senechal, a mathematician at Smith College in the United States, told AFP the discoveries were "exciting, surprising and amazing".
She said she expects the spectre and its relatives "will lead to a deeper understanding of order in nature and the nature of order."
Doris Schattschneider, a mathematician at Moravian College in the US, said both shapes were "stunning".
Even Nobel-winning mathematician Roger Penrose, whose previous best effort had narrowed the number of aperiodic tiles down to two in the 1970s, had not been sure such a thing was possible, Schattschneider said.
Penrose, 91, will be among those celebrating the new shapes during the two-day "Hatfest" event at Oxford University next month.
All involved expressed amazement that the breakthrough was achieved by someone without training in maths.
"The answer fell out of the sky and into the hands of an amateur -- and I mean that in the best possible way, a lover of the subject who explores it outside of professional practice," Kaplan said.
"This is the kind of thing that ought not to happen, but very happily for the history of science does happen occasionally, where a flash brings us the answer all at once."
F.Jackson--ThChM