RYCEF
0.5300


Eruptions of plasma piling atop one another, solar wind streaming out in exquisite detail -- the closest-ever images of our Sun are a gold mine for scientists.
Captured by the Parker Solar Probe during its closest approach to our star starting on December 24, 2024, the images were recently released by NASA and are expected to deepen our understanding of space weather and help guard against solar threats to Earth.
- A historic achievement –
"We have been waiting for this moment since the late Fifties," Nour Rawafi, project scientist for the mission at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, told AFP.
Previous spacecraft have studied the Sun, but from much farther away.
Parker was launched in 2018 and is named after the late physicist Eugene Parker, who in 1958 theorized the existence of the solar wind -- a constant stream of electrically charged particles that fan out through the solar system.
The probe recently entered its final orbit where its closest approach takes it to just 3.8 million miles from the Sun's surface -- a milestone first achieved on Christmas Eve 2024 and repeated twice since on an 88-day cycle.
To put the proximity in perspective: if the distance between Earth and the Sun measured one foot, Parker would be hovering just half an inch away.
Its heat shield was engineered to withstand up to 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit (1,370 degrees Celsius) -- but to the team's delight, it has only experienced around 2,000F (1090C) so far, revealing the limits of theoretical modeling.
Remarkably, the probe's instruments, just a yard (meter) behind the shield, remain at little more than room temperature.
- Staring at the Sun –
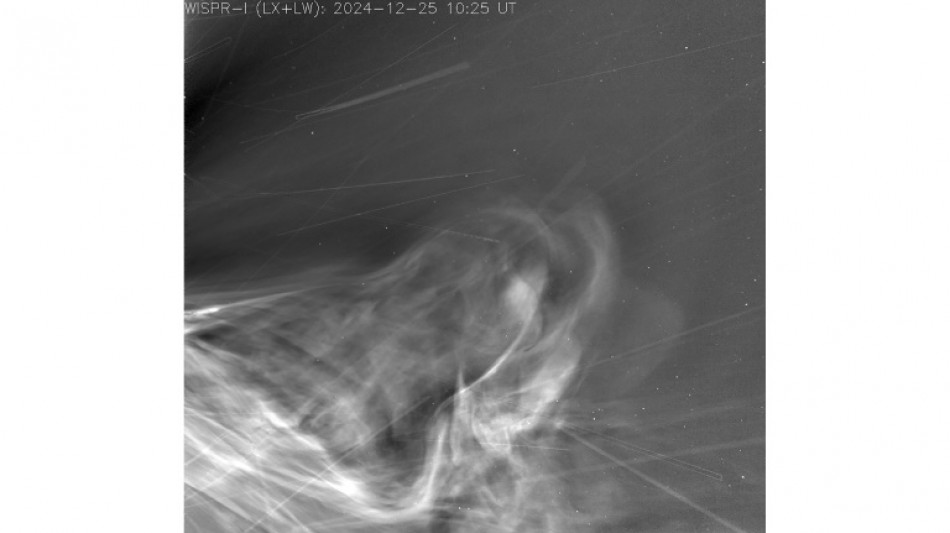
The spacecraft carries a single imager, the Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR), which captured data as Parker plunged through the Sun's corona, or outer atmosphere.
Stitched into a seconds-long video, the new images reveal coronal mass ejections (CMEs) -- massive bursts of charged particles that drive space weather -- in high resolution for the first time.
"We had multiple CMEs piling up on top of each other, which is what makes them so special," Rawafi said. "It's really amazing to see that dynamic happening there."
Such eruptions triggered the widespread auroras seen across much of the world last May, as the Sun reached the peak of its 11-year cycle.
Another striking feature is how the solar wind, flowing from the left of the image, traces a structure called the heliospheric current sheet: an invisible boundary where the Sun's magnetic field flips from north to south.
It extends through the solar system in the shape of a twirling skirt and is critical to study, as it governs how solar eruptions propagate and how strongly they can affect Earth.
- Why it matters –
Space weather can have serious consequences, such as overwhelming power grids, disrupting communications, and threatening satellites.
As thousands more satellites enter orbit in the coming years, tracking them and avoiding collisions will become increasingly difficult -- especially during solar disturbances, which can cause spacecraft to drift slightly from their intended orbits.
Rawafi is particularly excited about what lies ahead, as the Sun heads toward the minimum of its cycle, expected in five to six years.
Historically, some of the most extreme space weather events have occurred during this declining phase -- including the infamous Halloween Solar Storms of 2003, which forced astronauts aboard the International Space Station to shelter in a more shielded area.
"Capturing some of these big, huge eruptions...would be a dream," he said.
Parker still has far more fuel than engineers initially expected and could continue operating for decades -- until its solar panels degrade to the point where they can no longer generate enough power to keep the spacecraft properly oriented.
When its mission does finally end, the probe will slowly disintegrate -- becoming, in Rawafi's words, "part of the solar wind itself."
M.Chau--ThChM