CMSC
0.0084


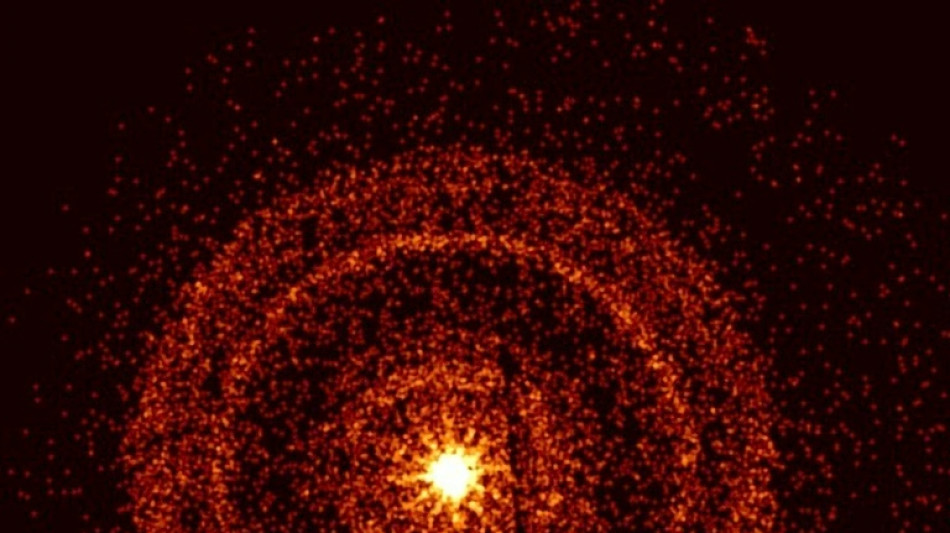
Astronomers have observed the brightest flash of light ever seen, from an event that occurred 2.4 billion light years from Earth and was likely triggered by the formation of a black hole.
The burst of gamma-rays -- the most intense form of electromagnetic radiation -- was first detected by orbiting telescopes on October 9, and its afterglow is still being watched by scientists across the world.
Astrophysicist Brendan O'Connor told AFP that gamma-ray bursts that last hundreds of seconds, as occurred on Sunday, are thought to be caused by dying massive stars, greater than 30 times bigger than our Sun.
The star explodes in a supernova, collapses into a black hole, then matter forms in a disk around the black hole, falls inside, and is spewed out in a jet of energy that travels at 99.99 percent the speed of light.
The flash released photons carrying a record 18 teraelectronvolts of energy -- that's 18 with 12 zeros behind it -- and it has impacted long wave radio communications in Earth's ionosphere.
"It's really breaking records, both in the amount of photons, and the energy of the photons that are reaching us," said O'Connor, who used infrared instruments on the Gemini South telescope in Chile to take fresh observations early Friday.
"Something this bright, this nearby, is really a once-in-a-century event," he added.
"Gamma-ray bursts in general release the same amount of energy that our Sun produces over its entire lifetime in the span of a few seconds -- and this event is the brightest gamma ray burst."
The gamma-ray burst, known as GRB 221009A, was first spotted by telescopes including NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, and Wind spacecraft on Sunday morning Eastern time.
- 1.9 billion-year-old movie -
It originated from the direction of the constellation Sagitta, and traveled an estimated 1.9 billion years to reach Earth -- less than the current distance of its starting point, because the universe is expanding.
Observing the event now is like watching a 1.9 billion-year-old recording of those events unfold before us, giving astronomers a rare opportunity to glean new insights into things like black hole formation.
"That's what makes this sort of science so addictive -- you get this adrenaline rush when these things happen," said O'Connor, who is affiliated with the University of Maryland and George Washington University.
He added that though the initial burst may have been visible to lucky amateur astronomers, it has since faded out of their view.
Over the coming weeks, he and others will continue watching for the signatures of supernovas at optical and infrared wavelengths, to confirm that their hypothesis about the origins of the flash are correct, and that the event conforms to known physics.
Unfortunately, while the initial burst may have been visible to amateur astronomers, it has since faded
Supernova explosions are also predicted to be responsible for producing heavy elements -- such as gold, platinum, uranium -- and astronomers will also be on the hunt for their signatures.
Astrophysicists have written in the past that the sheer power of gamma-ray bursts could cause extinction level events here on Earth.
But O'Connor pointed out that because the jets of energy are very tightly focused, and aren't likely to arise in our galaxy, this scenario is not something we should worry much about.
A.Kwok--ThChM