SCS
0.0200


Who were the first people to ride horses?
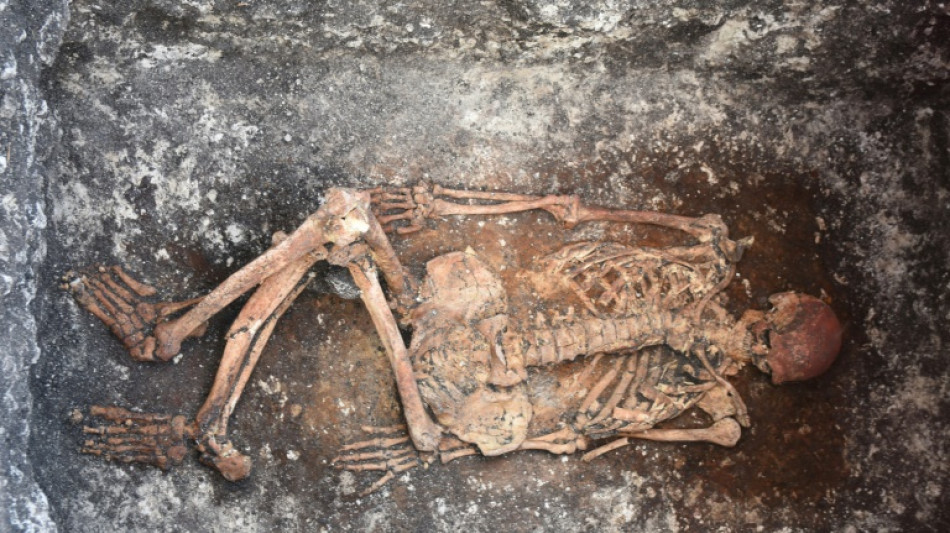
Researchers believe they have found the earliest evidence of horseback riding, by the ancient Yamnaya people in Europe some 5,000 years ago.
Their conclusions, based on an analysis of human skeletal remains found in Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania, were published on Friday in the journal Science Advances.
Domestication of horses for milk is widely accepted to have begun around 3500 BC to 3000 BC, the study said, but the "origins of horseback riding remain elusive."
The researchers from the University of Helsinki and other European institutions date the earliest horsemanship to 3000 BC to 2500 BC among members of the Yamnaya culture.
"Our findings provide a strong argument that horseback riding was already a common activity for some Yamnaya individuals as early as 3000 BC," the researchers said.
Horse bones have been discovered in Yamnaya settlements but they are not as well preserved as human skeletons, which were given proper burials in earth-covered mounds known as "kurgans."
The researchers said the human skeletons provided the best source of information about horse riding because any riding tack used by early riders would have been made using perishable materials.
The researchers said some of the human skeletons they analyzed bore skeletal traits indicative of what they called "horsemanship syndrome."
"A skeleton of a living person is reacting," Martin Trautmann, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki and one of the authors of the study, told AFP.
"If you sit on horseback you need to balance with every step of your mount, you need to cling tightly with your legs."
Doing that repeatedly leaves tell-tale changes in bone morphology, Trautmann said, including "stress-induced vertebral degeneration," a common ailment among avid horse riders.
"We know that saddles and stirrups dated much later," Trautmann said, and the early horse riders were probably riding bareback and gripping the mane of the horse.
- 'Cowboys, not warriors' -
Volker Heyd, a professor of archeology at the University of Helsinki, said the findings "fit very nicely into the overall picture" of Yamnaya culture.
"We were already suspecting them of using horses," Heyd said, and it could help explain the "exceptional" geographic expansion of their society in a few generations.
"It is difficult to envision how this expansion could have taken place without improved means of transport," the researchers said.
"Using horses for transport was a decisive step in human cultural development," they said.
"Trade and cultural exchange as well as conflicts and migrations leapt with the increase in speed and range provided by horsemanship."
The researchers said the Yamnaya were probably not initially using horses for warfare.
"They were cowboys, not warriors," said Trautmann.
Heyd said the early horse riders "were probably helping the Yamnaya people in guarding their animals, their cattle and sheep mostly."
According to the researchers, the earliest figurative evidence of horse riding comes from the Mesopotamian Ur III period shortly before 2000 BC through depictions of a horse and rider.
Images and mentions in cuneiform texts of horseback riding are also found in the Old Babylonian period from around 1880 BC to 1595 BC.
S.Wilson--ThChM