RBGPF
0.1000


Containing and cleaning up environmental pollution, especially in waterways, is crucial to controlling increasingly bullet-proof superbugs which could kill tens of millions by mid-century, a new UN report said Tuesday.
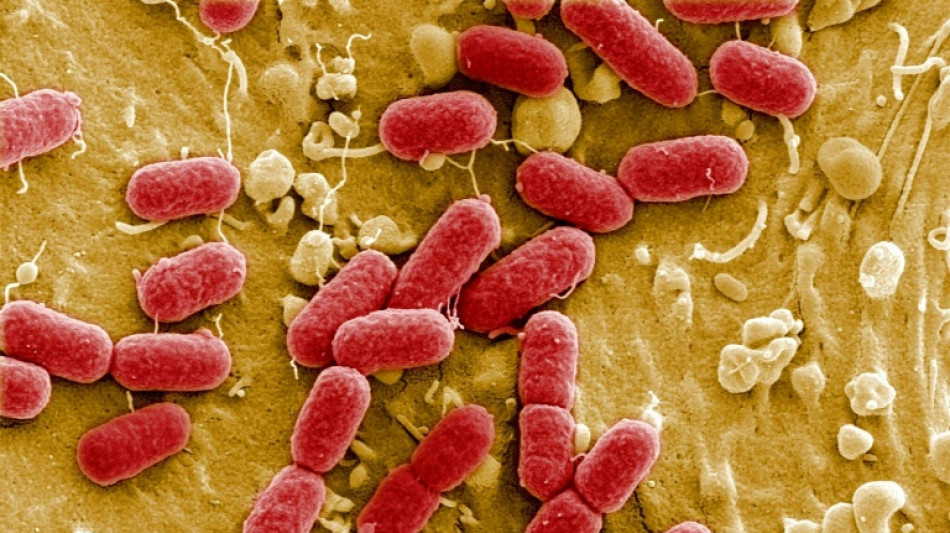
Superbugs -- strains of bacteria resistant to antibiotics -- are estimated to have killed 1.27 million people in 2019, and the World Health Organization says antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the top global health threats on the near-term horizon.
Up to 10 million deaths could occur every year by 2050 because of AMR, the UN says.
The disinfectants, antiseptics and antibiotics that can help microbes become stronger are everywhere, from toothpaste and shampoo to cow's milk and wastewater.
A new report Tuesday said pollution is a key driver in the "development, transmission and spread" of AMR, calling for urgent action to clean up the environment.
"With increasing pollution and lack of management of sources of pollution, combined with AMR in clinical and hospital settings and agriculture, risks are increasing," said the report from the UN Environment Programme.
Antimicrobial resistance is a natural phenomenon, but the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans, animals and plants has made the problem worse.
This means antibiotics may no longer work to fight the very infections they were designed to treat.
The UN report Tuesday said that pollution in the environment from key economic sectors has exacerbated the problem, namely from the pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing sectors, along with agriculture and health care.
Herbicides to control weeds on farms may also increase AMR, while heavy metals are also contributing to the problem.
Once antimicrobials enter the environment they seep into the food chain -- they've been found in fish and cattle -- and loop back into factories making everyday toiletries, for example.
- 'Silent pandemic' -
Antimicrobial resistant genes are in waterways across the globe, from the Ganges River in India to the Cache la Poudre River in the US state of Colorado, the UN study found.
"This is a real issue, because rivers are often the source of our drinking water," Jonathan Cox, senior lecturer in microbiology at Britain's Aston University, told AFP.
"It's already the silent pandemic," warned Cox, who is not linked to the UN study. "It is becoming the next pandemic without us really recognising it."
Prevention is key, the UN said.
"Fuelled by population growth, urbanisation and growing demand for food and healthcare, we can expect an increase in the use of antimicrobials and in pollutant releases into the environment," it said.
The UN urged governments and international groups to address "key pollution sources", including sewage, city waste, healthcare delivery, pharmaceutical manufacturing and intensive crop sectors.
Cox said solutions need to be global, since AMR is so pervasive.
One answer is to focus on clinical approaches, such as improving rapid testing for infections so that antibiotics are not incorrectly prescribed.
Another is improving wastewater management to remove antimicrobials. But such processes are complicated and costly.
"The technology is out there, it just isn't being employed because governments don't care so much about the environment as they do about the bottom line," Cox said.
P.Ho--ThChM